This post may contain affiliate links. Read our disclaimer policy.
Cooking oils are an essential part of our culinary adventures, adding flavor and richness to our dishes while imparting health benefits. With so many varieties available, it can be challenging to know which oil to use for specific cooking techniques. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various cooking oils, their characteristics, and when it’s best to use each one in your kitchen.
It is hard to envision a cooking pantry without cooking oils, especially my favorites; olive oil, avocado oil, and coconut oil.
What Are Some Common Types of Cooking Oils?
Olive Oil
Olive oil is a staple in Mediterranean cuisine and comes in various forms: extra virgin, virgin, light, and regular.
Extra virgin olive oil is the highest quality, obtained through cold pressing, and has a distinct fruity flavor and low acidity. It’s perfect for drizzling over salads, dipping bread, or using in dressings. Virgin olive oil works well in cooking at moderate temperatures, adding a delicate flavor to sautés and roasting.
Virgin Olive Oil: A close sibling of extra virgin, this variant works wonders for sautéing and roasting at moderate temperatures.
Canola Oil
Canola oil is a versatile and neutral-flavored oil extracted from rapeseed. Its high smoke point makes it suitable for frying, baking, and sautéing. It’s an excellent substitute for butter or vegetable oil in recipes, especially when you want a milder taste.
Vegetable Oil
Often a blend of different oils, vegetable oil is another all-purpose cooking oil. It has a high smoke point, making it suitable for frying and deep-frying. However, since its composition varies by brand, check the label for the specific oils used in the blend.
Sunflower Oil
Sunflower oil is rich in Vitamin E and has a mild flavor. It works well for sautéing, frying, and baking, and its light taste won’t overpower your dishes.
Peanut Oil
With a high smoke point and a distinctive nutty flavor, peanut oil is excellent for frying and stir-frying. It’s commonly used in Asian cuisines and adds an authentic taste to dishes like stir-fried noodles and tempura.
Sesame Oil
Both roasted and unroasted varieties are available. Roasted sesame oil has a robust, nutty flavor and is used as a finishing touch for Asian dishes. Unroasted sesame oil has a milder taste and can be used for cooking, particularly in stir-fries and marinades.
Corn Oil
Corn oil has a high smoke point, making it ideal for high-heat cooking like frying and grilling. It’s a good choice for recipes where a neutral flavor is desired.
Soybean Oil
Commonly labeled as “vegetable oil” in some regions, soybean oil is versatile and budget-friendly. Its mild flavor and high smoke point make it suitable for various cooking methods.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil has a distinct coconut flavor and is solid at room temperature. It’s a popular choice for baking, frying, and adding richness to curries and smoothies. Use it sparingly as it’s high in saturated fat. For high-heat cooking, choose refined coconut oil.
Avocado Oil
Avocado oil is packed with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and nutrients, making it a popular choice among health-conscious cooks.
Avocado oil has a high smoke point and a subtle buttery taste. It’s great for sautéing, grilling, and roasting vegetables, as well as for making dressings and marinades.

More Cooking Oils
Grapeseed Oil
Grapeseed oil has a light, neutral flavor and a high smoke point, making it suitable for frying and baking. It’s also a good source of Vitamin E.
Walnut Oil
Walnut oil has a rich, nutty flavor and is best used as a finishing oil in salads, pasta dishes, and baked goods. Avoid high-heat cooking, as it can become bitter.
Safflower Oil
Safflower oil is a heart-healthy option with a mild taste, making it suitable for various cooking methods, including frying, baking, and sautéing.
Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil is a rich source of Omega-3 fatty acids and has a nutty flavor. It’s best used in cold dishes, like salad dressings and dips, as it should not be heated.
Hempseed Oil
Similar to flaxseed oil, hempseed oil is high in Omega-3 fatty acids and has a nutty taste. Use it in dressings or drizzle it over cooked dishes.
Rice Bran Oil
Rice bran oil has a high smoke point and a light flavor, making it suitable for high-heat cooking and deep-frying.
Almond Oil
Almond oil has a subtle almond flavor and is best used in baking or as a finishing oil for salads and pastas.
Hazelnut Oil
Hazelnut oil adds a rich, nutty taste to your dishes and is perfect for drizzling over salads or desserts.
Pistachio Oil
Pistachio oil has a bold, nutty flavor and is best used as a finishing touch for salads, roasted vegetables, and even ice cream.
Macadamia Nut Oil
Macadamia nut oil has a buttery, delicate flavor and a high smoke point, making it suitable for sautéing and roasting.
My Favorite Cooking Oils
My favorite oils to cook with are olive oil (all types), avocado oil, and coconut oil. I will sometime use canola oil as well.
Olive oil is the main oil in my pantry. I use regular or virgin olive oil primarily for lite sautéing an grilling, and I use extra virgin olive oil primarily for marinades, salad dressings, or anything that requires a drizzle of oil.
When buying olive oil I look for the source of the olives. I try to buy the brands that are sole sourced, and not a blend of a few sources. This can sometime be difficult to find, and will be more expensive than blended olive oils.
Avocado oil is my choice for frying or sautéing and pan-searing at a higher temperature. You could also use canola oil for this, however, I prefer avocado oil because of its health benefits. Canola oil is the less expensive option.
For baking I primarily use coconut oil. It also work well when making pancakes or waffles.
What Are The Healthiest Cooking Oils?
Olive Oil
Benefits: Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which is associated with various health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and supporting weight management. It also contains antioxidants, such as vitamin E, which can help protect cells from oxidative damage.
Avocado Oil
Benefits: Avocado oil is another excellent source of monounsaturated fats and has a high smoke point, making it suitable for high-heat cooking. It also contains vitamin E and various phytonutrients that may have anti-inflammatory properties.
Coconut Oil
Benefits: Coconut oil is unique because it primarily consists of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are quickly metabolized for energy. It has been linked to potential benefits such as improved brain function, weight management, and antimicrobial properties. However, it’s important to use coconut oil in moderation due to its high saturated fat content.
Flaxseed Oil
Benefits: Flaxseed oil is an excellent source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for heart and brain health, and flaxseed oil is a suitable option for those following a plant-based diet.
Walnut Oil
Benefits: Walnut oil is rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and also contains other beneficial nutrients like antioxidants and phytosterols. Consuming walnut oil may help support heart health and reduce inflammation.
When using cooking oils, it’s essential to consider their smoke points and select the appropriate oil for the cooking method.
For high-heat cooking, oils with high smoke points like avocado oil or refined coconut oil are more suitable, while for drizzling over salads or low-heat cooking, olive oil and flaxseed oil are great options.
Additionally, moderation is key, as all oils are calorie-dense, and excessive consumption can lead to weight gain.
Choosing the Right Cooking Oils
Choosing the right cooking oils can enhance the taste and nutritional value of your dishes. Each oil brings unique flavors and qualities to the table, allowing you to experiment with various cuisines and cooking techniques.
Consider the smoke point, flavor, and health benefits of the oils to determine which one best suits your needs. With this comprehensive guide, you’re well-equipped to elevate your culinary creations and explore the vast world of cooking oils.
Mastering the art of cooking oils opens a world of culinary possibilities. Choose the right oil for each dish, and your recipes will burst with flavors that delight the palate. From the timeless elegance of olive oil to the tropical charm of coconut oil, each oil has its unique role to play in the kitchen.
By understanding cooking oils characteristics and using them correctly, you can transform your cooking and elevate every meal to new heights.
Cooking Oils Sources
- “Guide to Cooking Oils” – The Spruce Eats
- “The Ultimate Guide to Cooking Oils” – BBC Good Food
- “Cooking Oil Types and Uses” – Healthline
Recipes With Cooking Oils
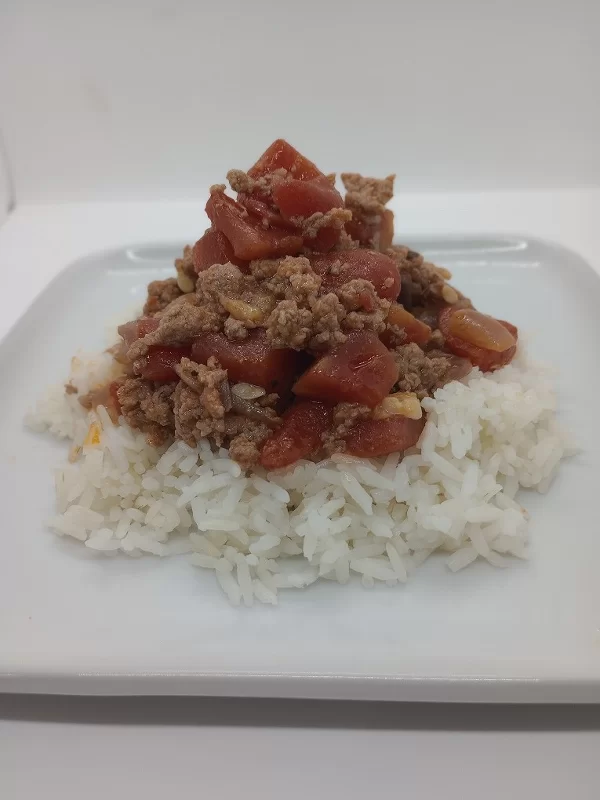

Ground Turkey and Zucchini
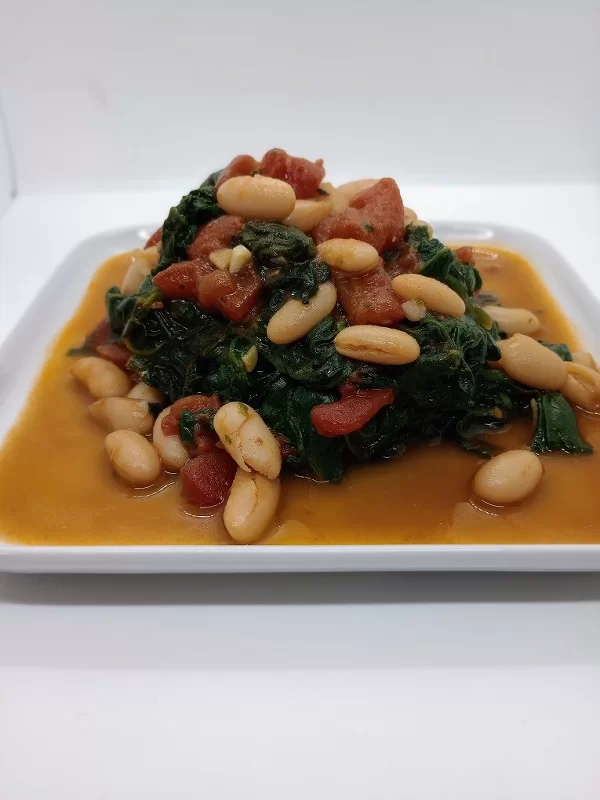

Cannellini Beans with Spinach and Tomatoes
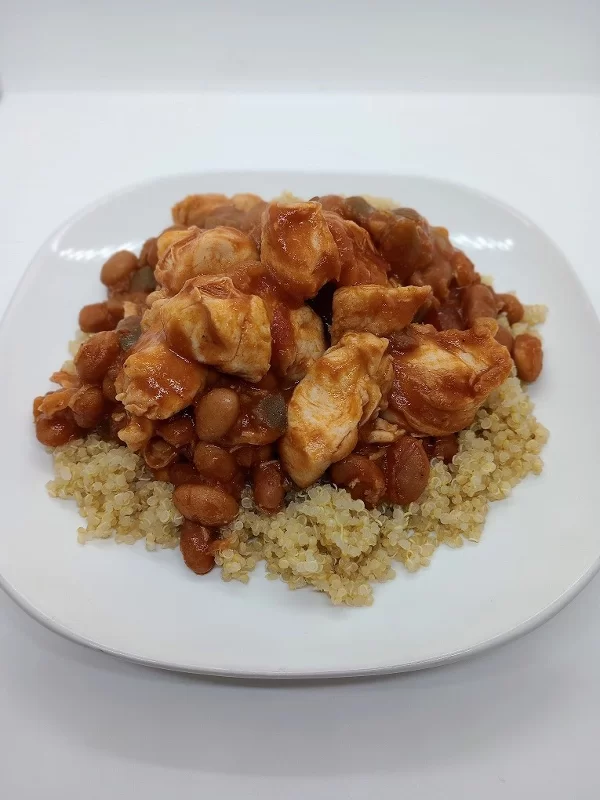

Salsa Chicken Recipe with Pinto Beans






